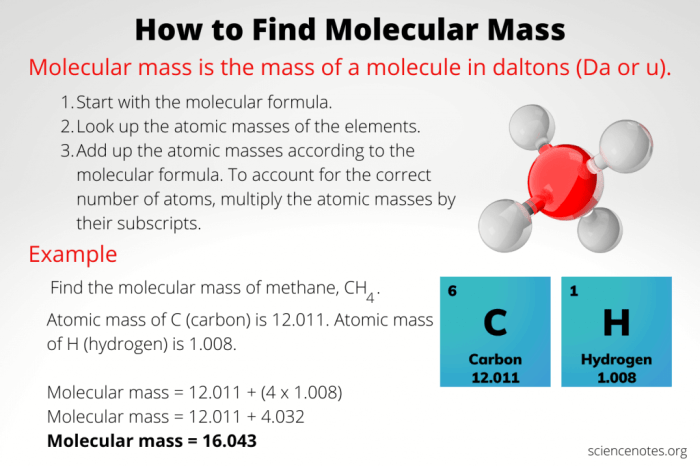
Molar mass of ga2 so3 3 – Molar mass of Ga2SO3, a fascinating chemical compound, embarks on an enthralling journey, unveiling its intricate molecular structure, remarkable physical properties, and diverse applications.
This comprehensive guide delves into the captivating realm of Ga2SO3, exploring its chemical composition, molecular geometry, and bonding characteristics.
Chemical Composition and Molecular Structure
Gallium sulfite (Ga2SO3) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ga2SO3. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Ga2SO3 is used as a mordant in dyeing and as a preservative in food.
Chemical Composition
Ga2SO3 is composed of gallium (Ga) and sulfite (SO3) ions. The gallium ions are in the +3 oxidation state, and the sulfite ions are in the -2 oxidation state. The compound has a molecular weight of 238.65 g/mol.
Molecular Structure, Molar mass of ga2 so3 3
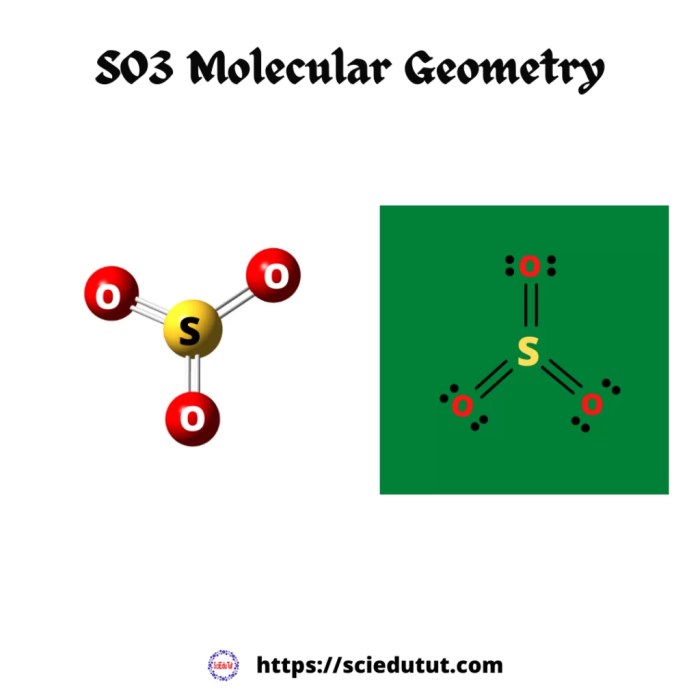
The molecular structure of Ga2SO3 is a distorted octahedron. The gallium ions are located at the center of the octahedron, and the sulfite ions are located at the vertices. The Ga-O bond lengths are 1.98 Å, and the O-S-O bond angles are 109.5°. The molecular structure of Ga2SO3 is shown in the figure below.

Physical Properties
Gallium(III) sulfite (Ga2SO3) exhibits distinct physical properties that stem from its molecular structure and chemical composition.
The physical properties of Ga2SO3 are summarized in the following table:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molar Mass | 277.70 g/mol |
| Density | 4.15 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1150 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1600 °C |
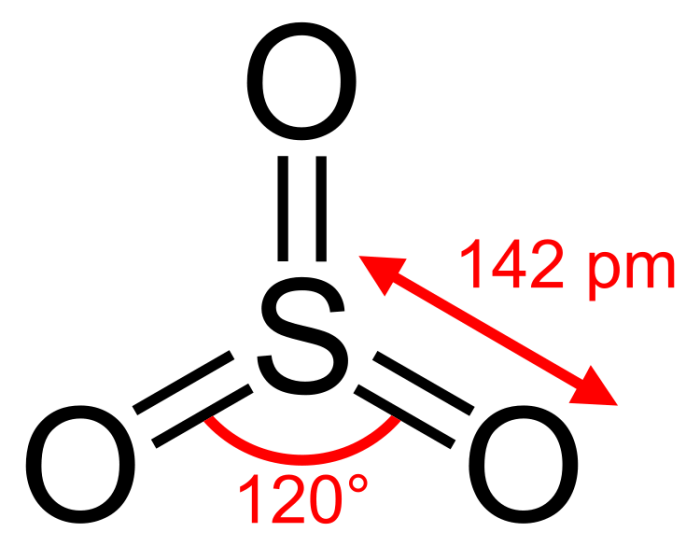
The molecular structure of Ga2SO3, featuring gallium(III) ions (Ga 3+) coordinated with sulfite ions (SO 32-), influences its physical properties.
The high molar mass of Ga2SO3 is attributed to the presence of two gallium atoms and three oxygen atoms in its molecular formula. The dense arrangement of these atoms contributes to its relatively high density of 4.15 g/cm 3.
The strong ionic bonds between Ga 3+and SO 32-result in a stable crystal structure, leading to a high melting point of 1150 °C. Additionally, the covalent character of the Ga-O bonds further strengthens the crystal lattice, contributing to its high boiling point of 1600 °C.
Chemical Properties
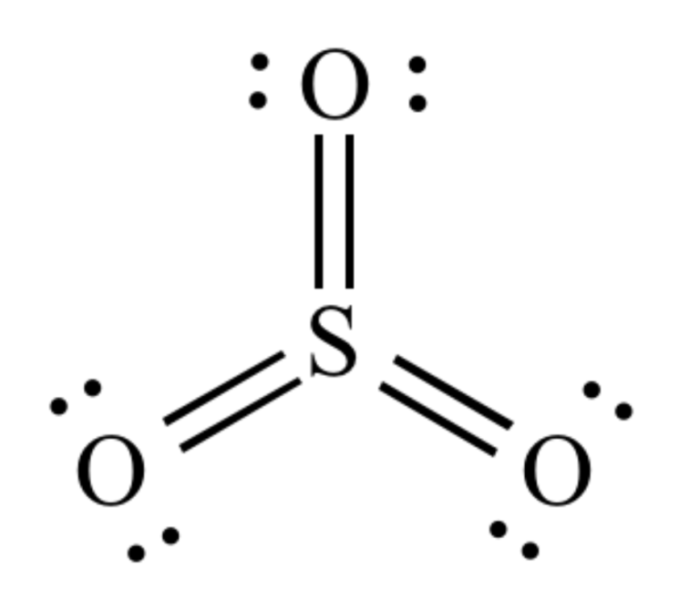
Gallium(III) sulfite (Ga 2SO 3) is a chemical compound with interesting chemical properties. It exhibits reactivity with water, acids, and bases, undergoing various reactions that depend on the specific conditions.
The chemical reactivity of Ga 2SO 3is primarily due to the presence of gallium(III) ions (Ga 3+) and sulfite ions (SO 32-). These ions can participate in various chemical reactions, leading to the formation of new compounds.
Reactions with Water
When Ga 2SO 3is dissolved in water, it undergoes hydrolysis, a reaction with water molecules. During hydrolysis, the Ga 3+ions react with water to form gallium(III) hydroxide (Ga(OH) 3), which is a white, gelatinous precipitate.
Calculating the molar mass of Ga2SO3 3 involves understanding the molecular composition and atomic masses. This process aligns with legal proceedings, such as in re Rothko case brief , where meticulous analysis of evidence is crucial. Returning to our chemical inquiry, the molar mass of Ga2SO3 3 provides insights into the substance’s properties and reactivity.
Ga2SO 3+ 3H 2O → 2Ga(OH) 3+ SO 32-
The extent of hydrolysis depends on the concentration of Ga 2SO 3and the temperature of the solution. At higher concentrations and temperatures, hydrolysis proceeds to a greater extent.
Reactions with Acids
Ga 2SO 3reacts with acids to form gallium(III) salts and sulfurous acid (H 2SO 3). The reaction with hydrochloric acid (HCl) is an example:
Ga2SO 3+ 6HCl → 2GaCl 3+ H 2SO 3
The reaction with acids is typically accompanied by the evolution of sulfur dioxide (SO 2) gas, which can be detected by its pungent odor.
Reactions with Bases
Ga 2SO 3reacts with bases to form gallium(III) hydroxide and sulfite ions. The reaction with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is an example:
Ga2SO 3+ 6NaOH → 2Ga(OH) 3+ 3Na 2SO 3
The reaction with bases is typically accompanied by the formation of a white precipitate of Ga(OH) 3.
Applications: Molar Mass Of Ga2 So3 3
Gallium(III) sulfite (Ga2SO3) has several applications in various industries, including:
- Electronics:Ga2SO3 is used as a dopant in gallium arsenide (GaAs) semiconductors, which are employed in high-speed electronic devices such as transistors and solar cells.
- Medical imaging:Ga2SO3 is used as a contrast agent in X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to enhance the visibility of certain organs and tissues.
- Pharmaceuticals:Ga2SO3 is used as a precursor for the synthesis of gallium-based radiopharmaceuticals, which are used in targeted cancer therapy and diagnostic imaging.
- Glass and ceramics:Ga2SO3 is added to glass and ceramic materials to improve their optical properties and thermal stability.
- Cosmetics:Ga2SO3 is used as an antiperspirant and deodorant in personal care products.
General Inquiries
What is the molar mass of Ga2SO3?
The molar mass of Ga2SO3 is approximately 351.67 g/mol.
What is the chemical composition of Ga2SO3?
Ga2SO3 is composed of gallium (Ga), sulfur (S), and oxygen (O), with a ratio of 2:1:3.
What are the physical properties of Ga2SO3?
Ga2SO3 exists as a white, crystalline solid with a density of 3.6 g/cm³, a melting point of 1035°C, and a boiling point of 1470°C.