Embark on an exploration of codominant/incomplete dominance practice worksheet answers, where the intricacies of genetics unfold in a captivating narrative. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts, inheritance patterns, and real-world applications of these genetic phenomena, providing a thorough understanding for students and professionals alike.
Delving into the intricacies of codominance and incomplete dominance, this guide unravels the complexities of genetic inheritance. Discover the fascinating examples of these phenomena in nature, unravel the underlying genetic principles, and gain insights into their significance in genetic engineering and agriculture.
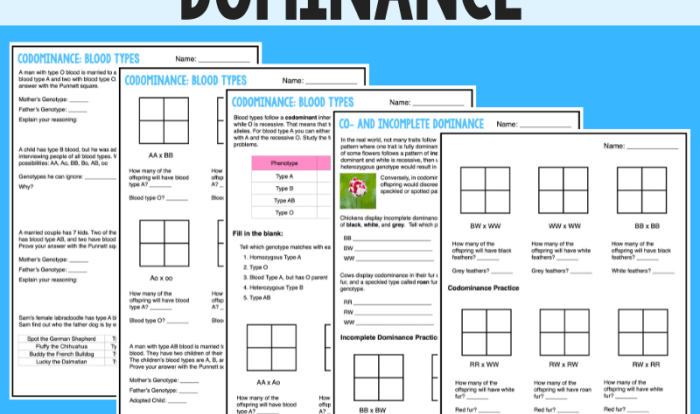
Definitions: Codominant/incomplete Dominance Practice Worksheet Answers
Codominanceoccurs when two alleles of a gene are both expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygous individual.
Examples of codominanceinclude the ABO blood group system in humans, where individuals with the A allele and the B allele have both A and B antigens on their red blood cells, resulting in the AB blood type.
Incomplete dominanceis a type of inheritance in which neither allele of a gene is dominant, resulting in an intermediate phenotype.
Inheritance Patterns
Codominance, Codominant/incomplete dominance practice worksheet answers
In codominance, the heterozygous genotype has a distinct phenotype that is different from both homozygous genotypes.
Punnett squareis a tool used to predict the inheritance patterns in codominance. In a Punnett square, the alleles of one parent are listed along the top, and the alleles of the other parent are listed along the side. The resulting squares represent the possible genotypes of the offspring.
Heterozygous individualshave two different alleles of a gene, while homozygous individualshave two identical alleles of a gene.
Incomplete Dominance
In incomplete dominance, the heterozygous genotype has a phenotype that is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygous genotypes.
Examples of incomplete dominanceinclude the flower color in snapdragons, where the homozygous red genotype produces red flowers, the homozygous white genotype produces white flowers, and the heterozygous genotype produces pink flowers.
Examples and Applications

Codominance, Codominant/incomplete dominance practice worksheet answers
- ABO blood group systemin humans
- Flower colorin snapdragons
- Feather colorin chickens
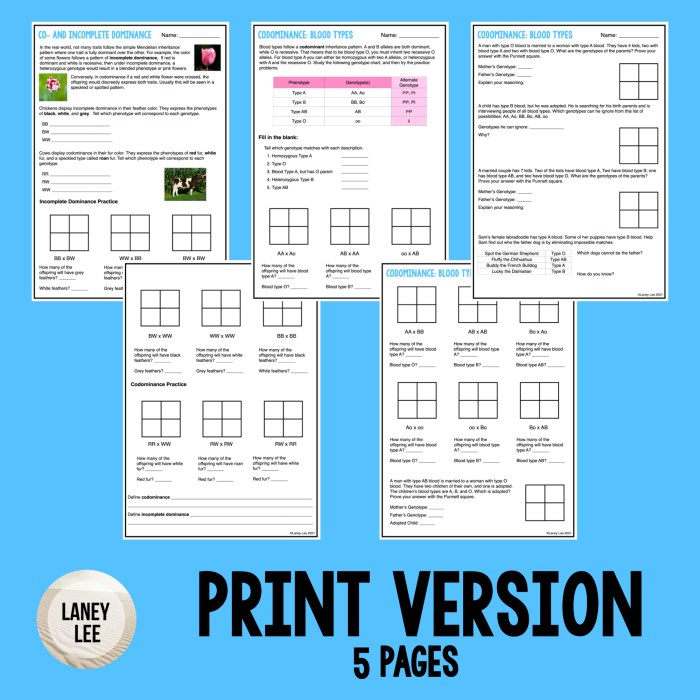
Applications of codominanceinclude:
- Genetic engineeringto create organisms with desired traits
- Agricultureto improve crop yields and resistance to pests and diseases
FAQ
What is the difference between codominance and incomplete dominance?
Codominance occurs when both alleles of a gene are fully expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygous individual, while incomplete dominance occurs when neither allele is fully dominant and the phenotype is a blend of both alleles.
How can I use a Punnett square to predict the inheritance patterns of codominant/incomplete dominant traits?
A Punnett square is a diagram that shows all possible combinations of alleles that can be inherited from parents. It can be used to predict the probability of inheriting a particular genotype or phenotype.
What are some real-world examples of codominance and incomplete dominance?
Codominance is observed in the ABO blood group system in humans, where individuals with both A and B alleles have type AB blood. Incomplete dominance is observed in the flower color of snapdragons, where individuals with both red and white alleles have pink flowers.