Relias Dysrhythmia Basic A 35 Questions delves into the intricacies of electrocardiography (ECG) and dysrhythmia identification, providing a comprehensive guide for healthcare professionals. Understanding dysrhythmias is paramount in healthcare, as it enables the timely detection and management of potentially life-threatening conditions.
This Artikel encompasses the fundamental principles of ECG, the criteria for dysrhythmia classification, and the principles of assessment and management. Case studies and clinical applications further enhance the learning experience, equipping readers with practical knowledge for patient care.
Definition and Overview of Dysrhythmia
Dysrhythmia, also known as arrhythmia, refers to any abnormal heart rhythm. It can be caused by various factors, including structural heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, and medications. Common types of dysrhythmias include bradycardia (slow heart rate), tachycardia (fast heart rate), and arrhythmias associated with atrial or ventricular dysfunction.
Understanding dysrhythmias is crucial in healthcare as they can lead to serious complications, such as heart failure, stroke, or sudden cardiac death. Early detection and management of dysrhythmias are essential to prevent adverse outcomes.
Basic Principles of Electrocardiography (ECG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart. It is recorded using electrodes placed on the chest, limbs, and back.
An ECG consists of a series of waves and intervals that correspond to the electrical impulses generated by the heart. The P wave represents atrial depolarization, the QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, and the T wave represents ventricular repolarization. The intervals between these waves, such as the PR interval and QT interval, provide valuable information about the conduction system of the heart.
ECG interpretation techniques involve analyzing the morphology, duration, and timing of these waves and intervals to identify any abnormalities that may indicate dysrhythmias or other heart conditions.
Identification and Classification of Dysrhythmias
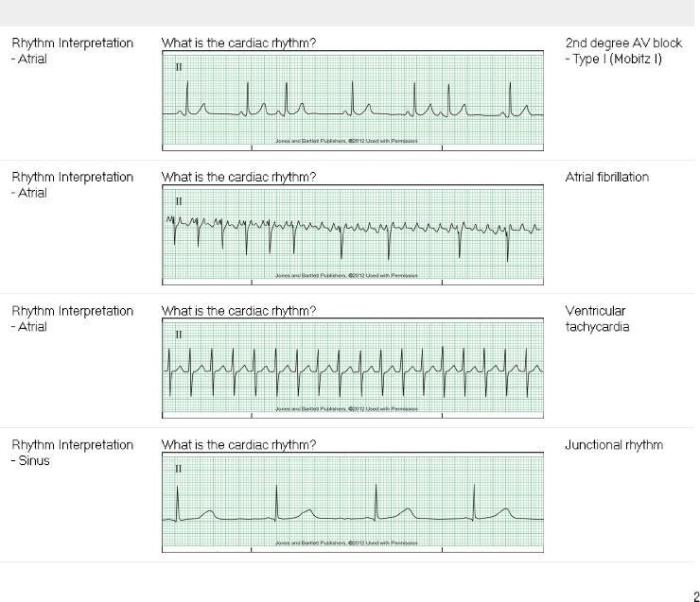
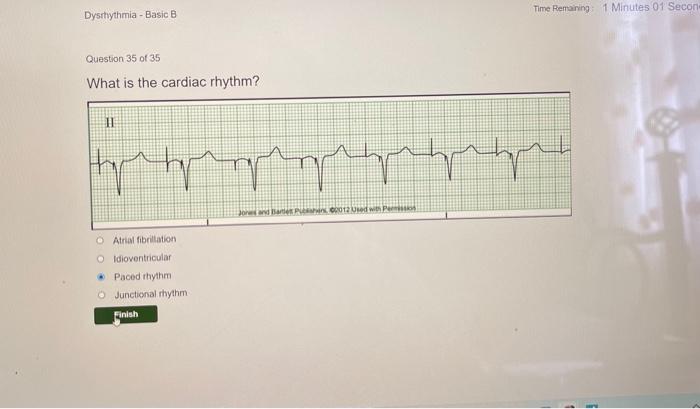
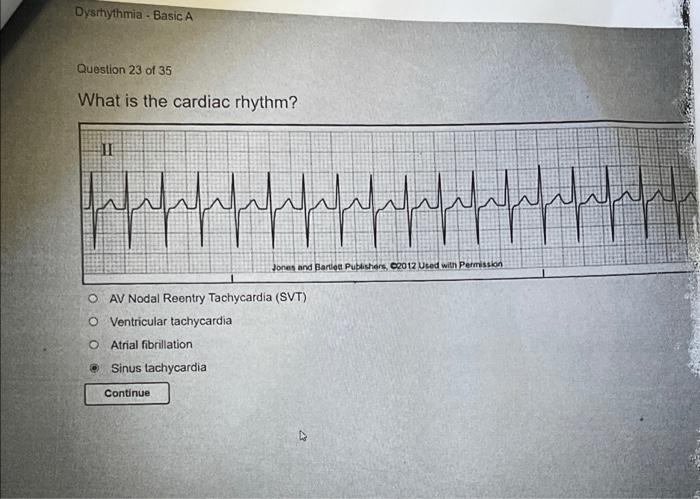
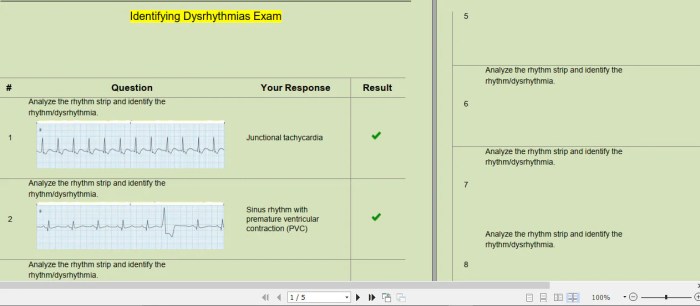
Dysrhythmias are identified and classified based on specific criteria, including heart rate, QRS complex morphology, and the presence of atrial or ventricular activity.
Supraventricular arrhythmias originate above the ventricles and include conditions such as sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and atrial flutter. Ventricular arrhythmias originate within the ventricles and include conditions such as ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and premature ventricular contractions.
Each type of dysrhythmia has its own characteristic ECG findings, which are essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Assessment and Management of Dysrhythmias
Assessing a patient with dysrhythmia involves obtaining a detailed medical history, performing a physical examination, and reviewing an ECG.
Management of dysrhythmias depends on the type of arrhythmia, its severity, and the underlying cause. Treatment options may include medications to control heart rate or rhythm, cardiac pacing to regulate electrical impulses, or surgical interventions to correct structural heart defects.
Nurses play a vital role in monitoring patients with dysrhythmias, administering medications, and providing patient education and support.
Questions Often Asked: Relias Dysrhythmia Basic A 35 Questions
What is the significance of understanding dysrhythmias in healthcare?
Understanding dysrhythmias is crucial as they can indicate underlying heart conditions, potentially leading to life-threatening complications. Early identification and management are essential to prevent adverse outcomes.
How are dysrhythmias classified?
Dysrhythmias are classified based on their origin (supraventricular or ventricular), rate, and regularity. The criteria for classification include P wave morphology, QRS complex duration, and the presence of specific intervals.
What are the common types of dysrhythmias?
Common dysrhythmias include sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
What is the role of nurses in managing dysrhythmias?
Nurses play a vital role in monitoring patients with dysrhythmias, assessing their condition, administering medications, and providing patient education. They also collaborate with physicians to develop and implement appropriate management plans.