Select a good design recommendation for text hyperlinks. – Design Recommendations for Effective Text Hyperlinks takes center stage, offering a comprehensive guide to enhancing the user experience through well-crafted hyperlinks. This guide explores principles for selecting hyperlink text, styling considerations, strategic placement, and accessibility best practices, empowering web designers to create hyperlinks that are both visually appealing and functionally effective.
Hyperlink Text

Selecting appropriate hyperlink text is crucial for effective web design. The text should be clear, concise, and accurately represent the destination.
Design Principles:
- Use descriptive text that indicates the purpose of the link.
- Avoid generic or vague terms like “click here” or “read more”.
- Keep hyperlink text concise to prevent overcrowding and confusion.
Accessibility Considerations:
- Ensure hyperlink text is screen reader-friendly for users with visual impairments.
- Provide alternative text for images used as hyperlinks.
Hyperlink Style

Consistent hyperlink styling enhances website aesthetics and user experience.
Color and Font Considerations:
- Choose colors that contrast with the background to improve visibility.
- Use a legible font that is consistent with the website’s overall design.
Underline and Hover Effects:
- Underlining hyperlinks is a traditional convention that indicates clickable text.
- Hover effects can provide visual feedback when users hover over a hyperlink.
Consistent Hyperlink Styling:
- Apply the same hyperlink styling throughout the website to create a cohesive experience.
- Consider using CSS classes to simplify styling and maintain consistency.
Hyperlink Placement
Strategic placement of hyperlinks optimizes user flow and engagement.
Strategic Placement:
- Place hyperlinks within relevant text or context to guide users to the intended destination.
- Avoid distracting or overwhelming users with excessive hyperlinks.
Ensuring Identifiability:
- Use contrasting colors or styles to make hyperlinks easily identifiable.
- Consider using icons or images to indicate clickable elements.
Hyperlink Context

Providing clear context for hyperlinks enhances user comprehension and navigation.
Clear and Concise Context:
- Provide a brief description of the destination before the hyperlink.
- Use descriptive hyperlink text to indicate the target of the link.
Avoiding Generic Text:
- Avoid using generic or vague hyperlink text that does not provide sufficient information.
- Instead, use specific and descriptive terms to guide users to the intended destination.
Hyperlink Organization: Select A Good Design Recommendation For Text Hyperlinks.
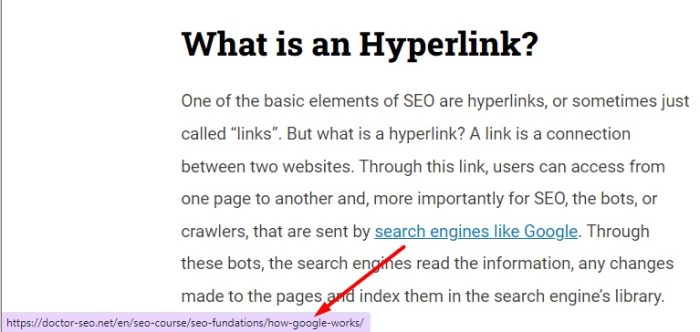
Organizing hyperlinks into categories improves navigation and accessibility.
HTML Tables:
- Use HTML tables to group hyperlinks into logical categories.
- This provides a structured and organized way to present hyperlinks.
Separate Sections:
- Create separate sections for different types of hyperlinks, such as internal, external, or resource links.
- This helps users easily locate the desired information.
Bullet Points:
- Use bullet points to list hyperlinks for easy navigation and readability.
- This format makes it simple for users to scan and select the relevant hyperlink.
Hyperlink Accessibility
Ensuring hyperlinks are accessible to users with disabilities is essential for inclusive web design.
Screen Reader-Friendly Text:
- Use hyperlink text that is easy for screen readers to interpret.
- Avoid using images or icons as hyperlinks without providing alternative text.
Alternative Text for Images:
- Provide meaningful alternative text for images used as hyperlinks.
- This ensures that users with visual impairments can understand the purpose of the hyperlink.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key design principles for selecting hyperlink text?
Hyperlink text should be concise, descriptive, and accurately represent the destination page. Avoid generic terms or vague language, and ensure that the text is easily readable and distinguishable from the surrounding content.
How can I ensure that my hyperlinks are accessible to users with disabilities?
Use screen reader-friendly hyperlink text, provide alternative text for images used as hyperlinks, and ensure that hyperlinks are keyboard accessible. Additionally, consider using HTML tables or separate sections to organize hyperlinks for easy navigation.